Why the module?
On any Drupal projects, you may face this kind of logs:
PHP Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 134217728 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 6369280 bytes) in ...
This happens when a PHP process is reaching his memory limit and cannot achieve the task it has been requested. Multiple situations can be the reason of this error. From image manipulations to migrations or wrong designed code for example. Before updating the memory allocated to PHP, it is always better to investigate the process causing the issue as increasing the memory may be a temporary patch before the new limit is reached in case the root cause is code design.
However, there are some operation like image manipulation, media upload, etc which are valid scenarios that require more memory for PHP processes. The most straightforward fix is to increase the memory limit allowed per PHP process. This is valid if your entire application is memory consuming and globally require more memory. But in most of the cases, these are very specific operations which are reaching the limit. Increasing the memory globally is not a good idea as it means less PHP processes in parallel. In short, if PHP has access to 1G and is configured to grant 512M to each PHP process, that would mean your application can only serve 2 requests in parallel. Keeping the memory limit to 128M and conditionally increasing the limit to 512M for the few expensive processes is a much better use of the available memory.
What the module offers?
This is where I introduce Memory Limit Policy module which can be used to configure policies to conditionally increase the memory limit.
At the time I write this post, it comes with different plugins to alter the memory based on:
- The path
- The presence of a query argument
- The user role
- The route name
- The HTTP method
- The Drush command (please note that it comes with some limitation).
Plugins can be combined to be more restrictive on when to change the memory limit. It is designed to be easy to extend as policies are plugins which mean you can create your own policy if your conditions are very specific.
How to configure the module?
Let’s quickly dive into the module configuration and say we want to increase the memory allocated to the process which generate image presets to 256M.
Once the module is enabled, policies are listed in Configuration > Performance > Memory Limit Policy > Policies (/admin/config/performance/memory-limit-policy/list).
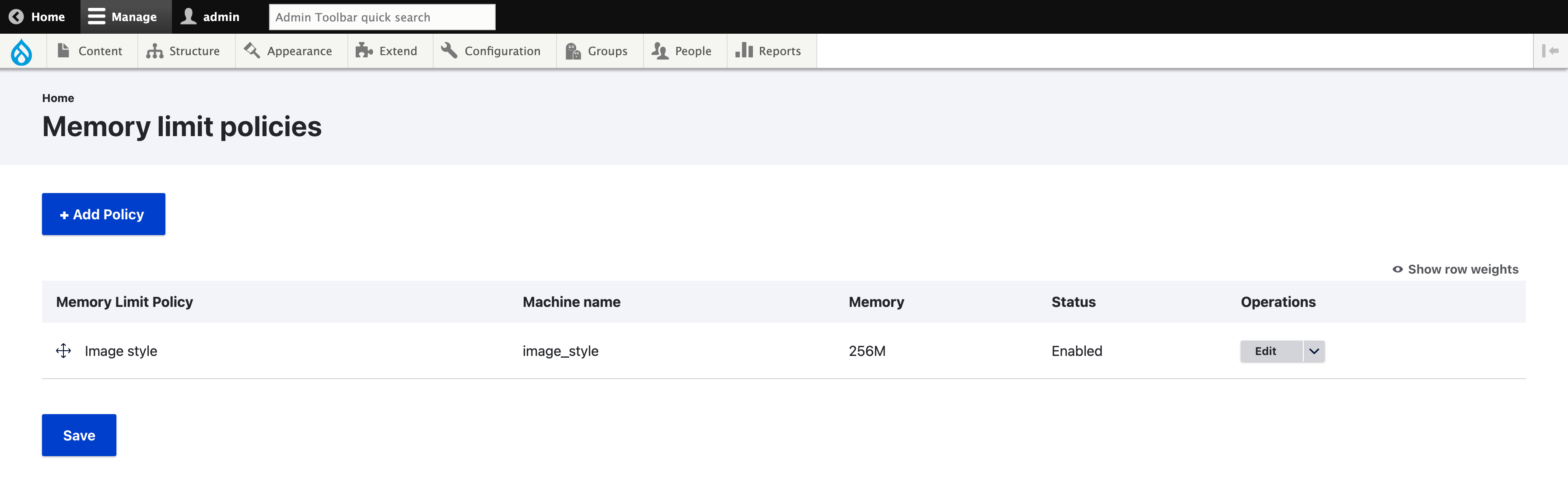
To create a new policy, click the “+ Add Policy” button.
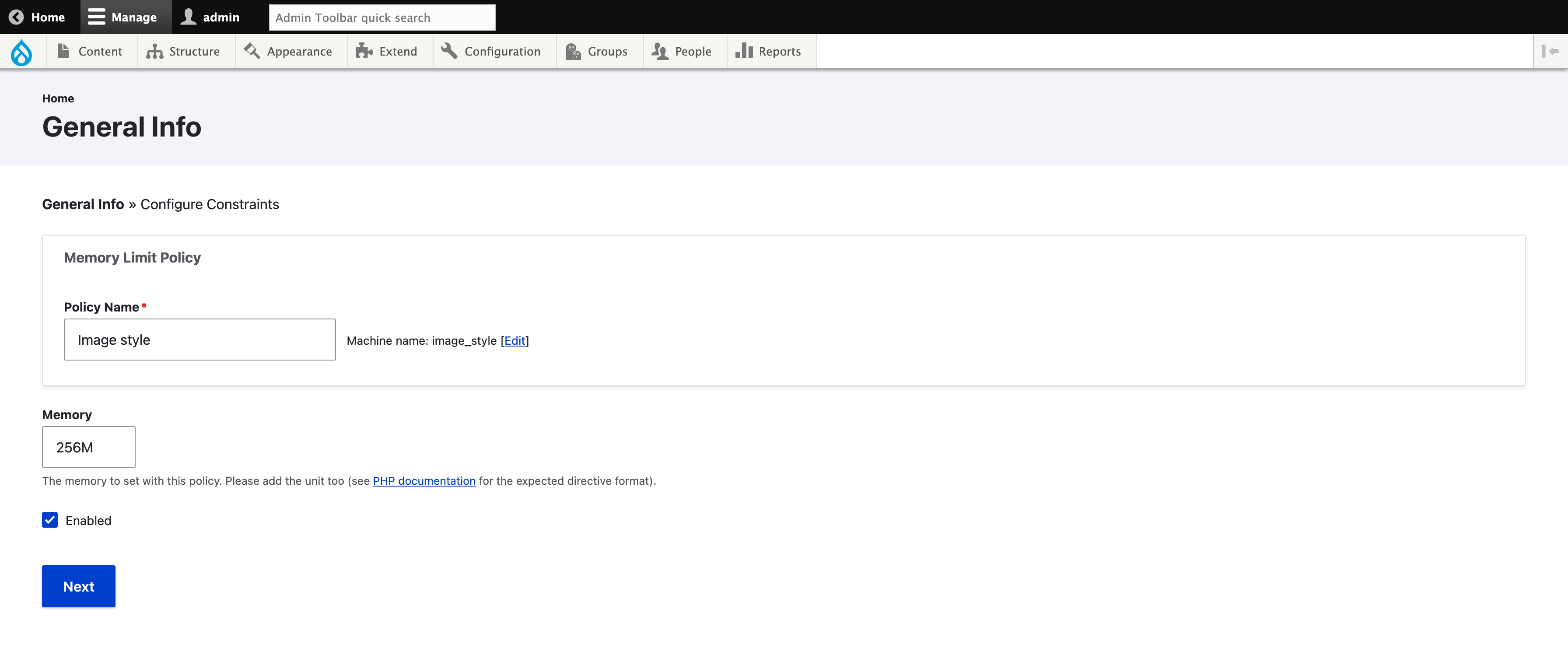
It displays the first step of the policy configuration. You must give a name to the policy (“Image style” in our example) and choose the memory that the policy will apply when the conditions are met (“256M” in our example). The format must respect the shorthand byte format. 100K for 100 kilobytes, 100M for 100 megabytes and 1G for 1 gigabytes. This is the same format which is used in php.ini to configure the global memory limit.
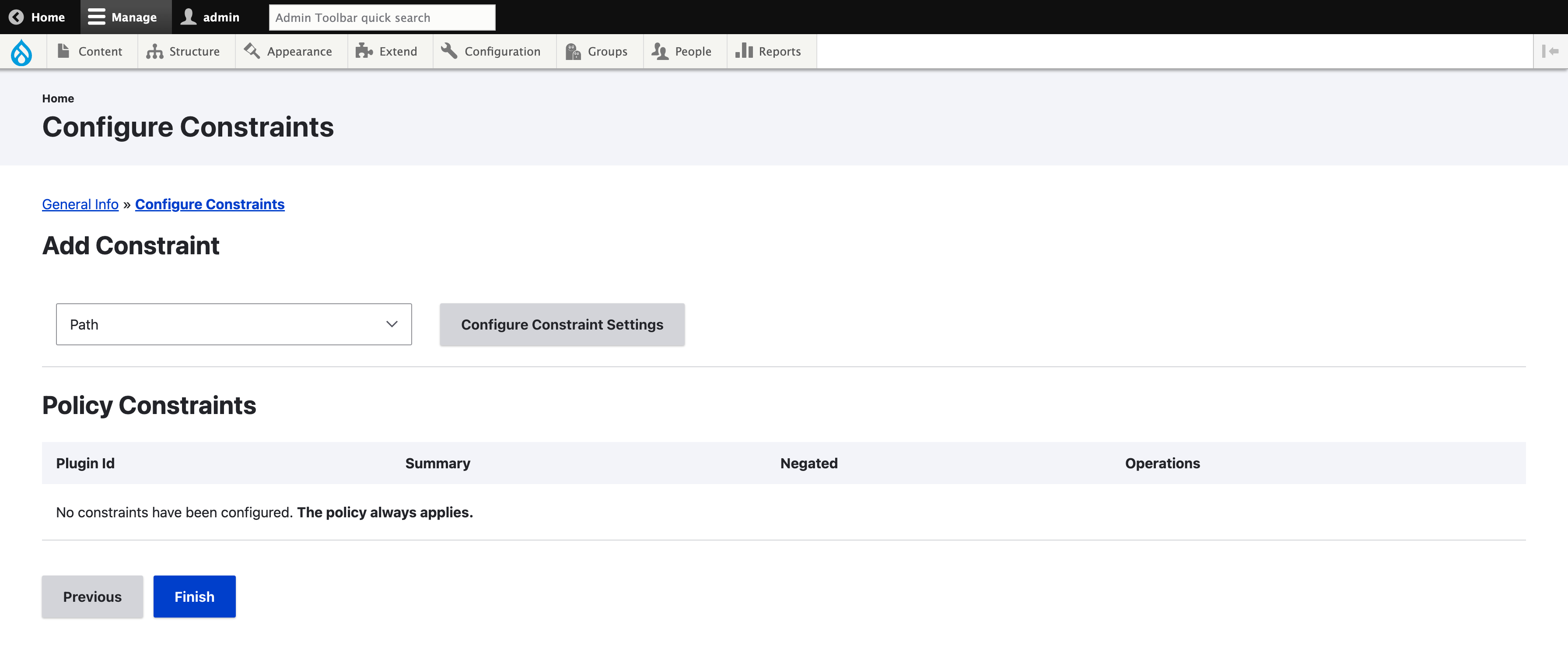
The second step of the policy setup is to configure the constraints which determine if the policy applies. Be sure to enable some Memory Limit Policy sub-modules which provide some constraint method or to create your own one. If you don’t configure any constraint, the policy will always apply. If that is really what you want to do, probably using a module is not the best choice and update the PHP configuration globally is a better one.
Each constraint will come with its own configuration form. It is possible to negate the constraint. For example, if you need to increase the memory on all frontend pages but not on the admin ones, it can be achieved by using the “Path” constraint with “/admin/” and the negate option. In our example, we will use the “Path” constraint and enter “/sites/default/files/styles/” as the path.
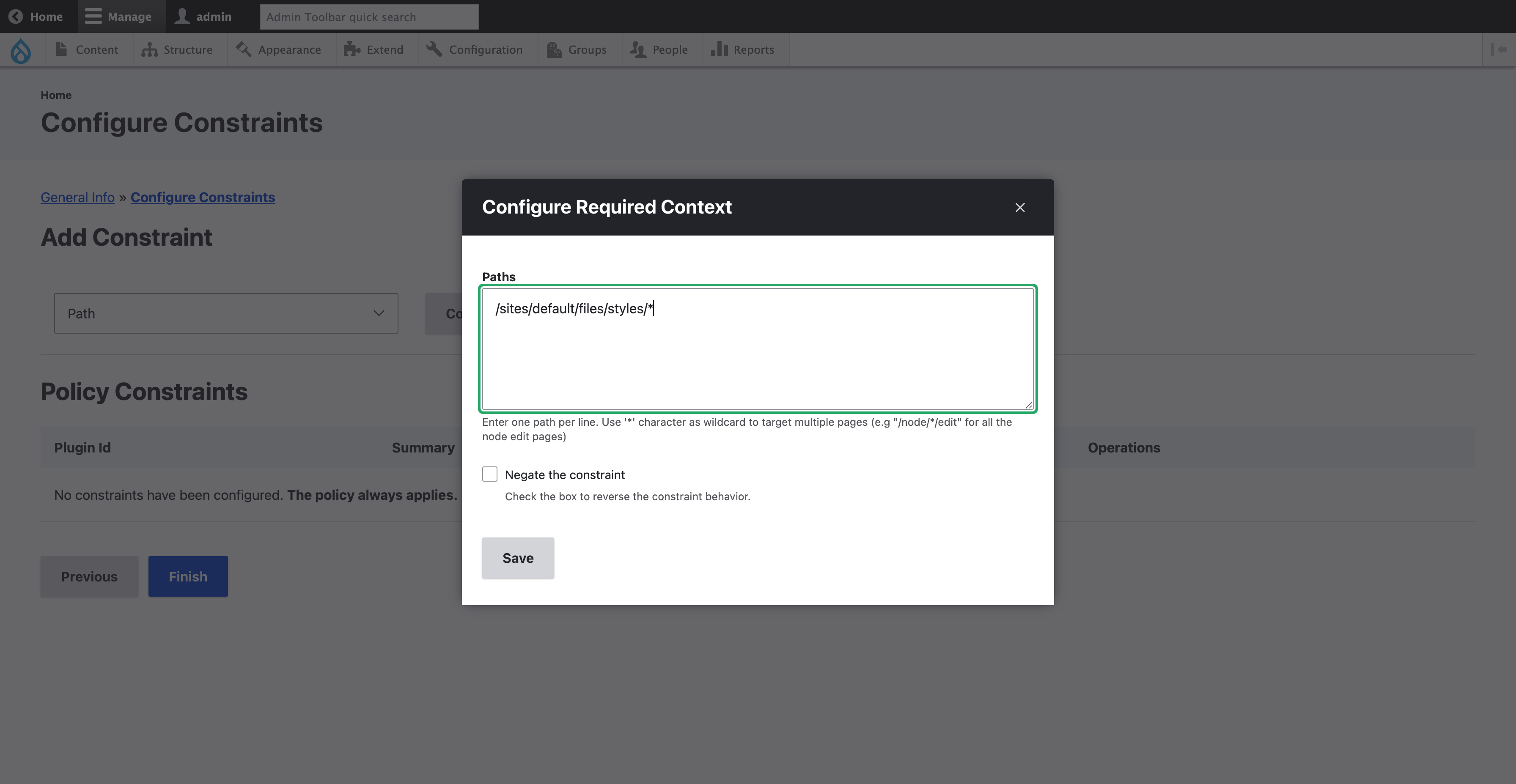
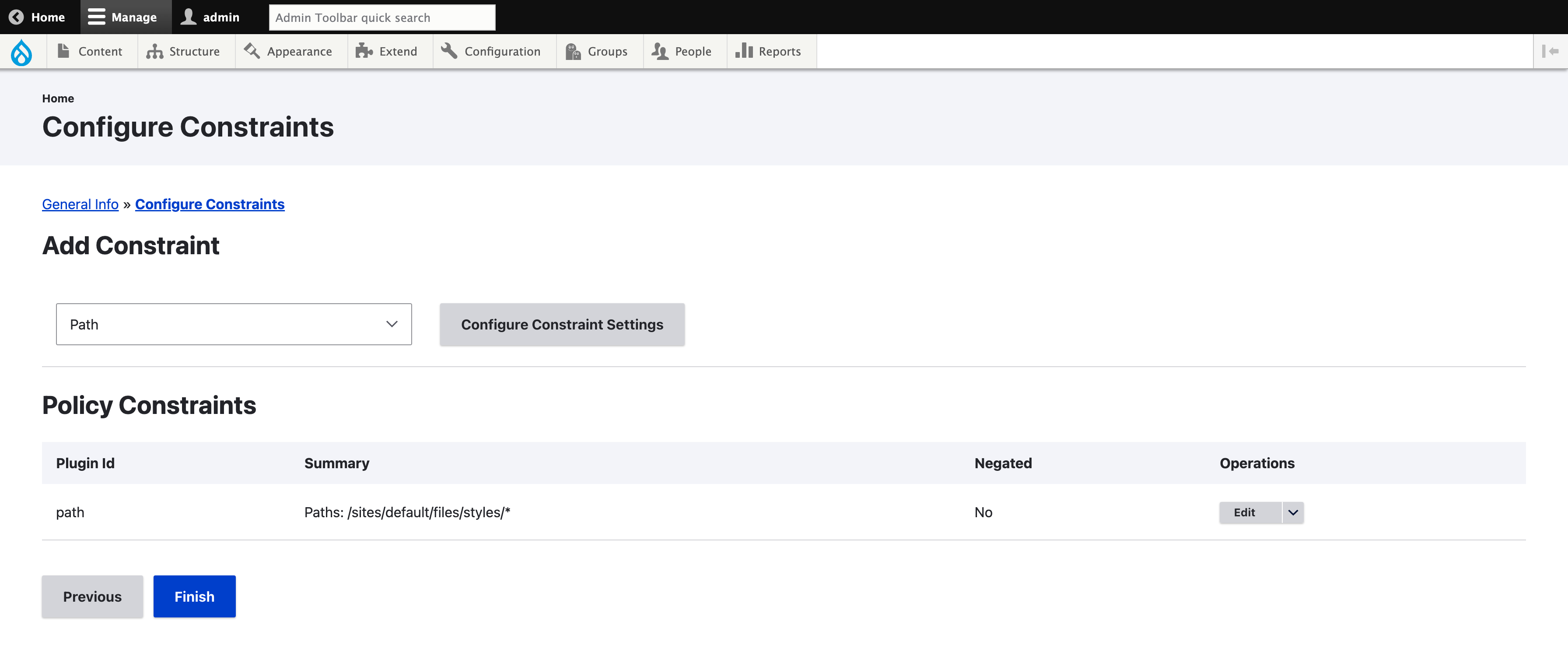
Finally, click the “Finish” button to get the constraints saved. The policy is now listed.
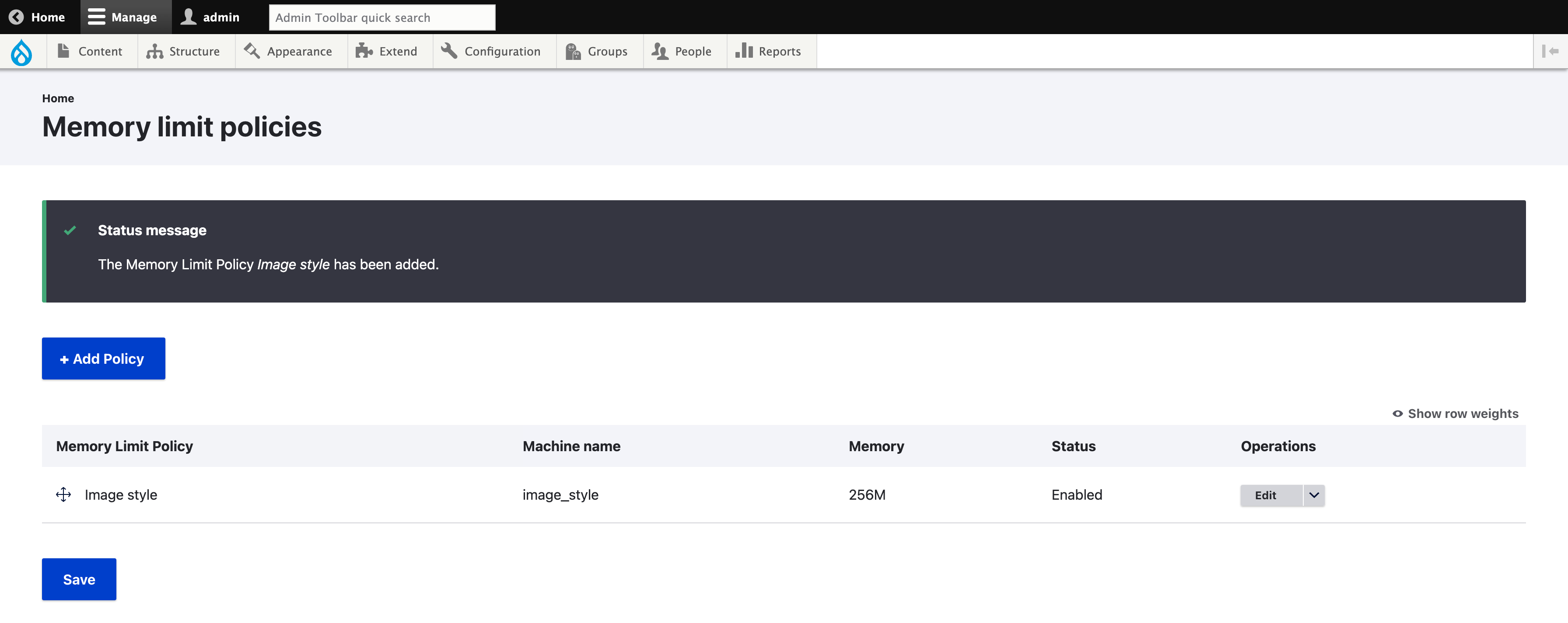
All the policies listed will be evaluated. In some situation, it may be needed to order the policies using drag & drop.
For some complex cases, it may be difficult to evaluate if a policy apply. To validate a policy is applied, we can use the setting to add the memory information in the headers. The setting can be set in Configuration > Performance > Memory Limit Policy > Configuration (/admin/config/performance/memory-limit-policy/settings).
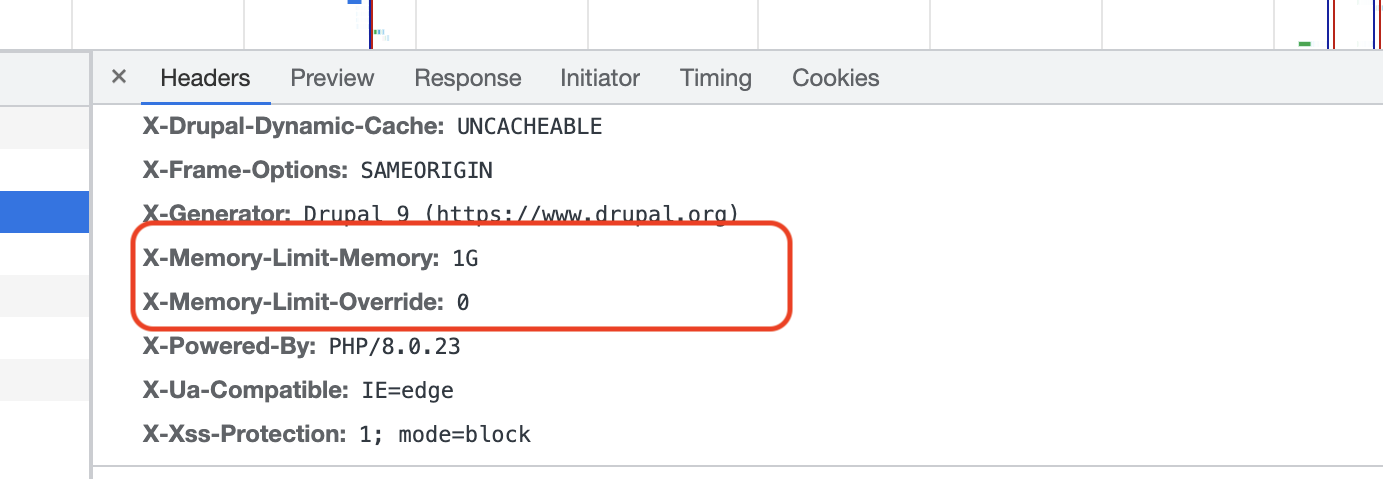
If no policy applies, headers will only indicate the default memory limit.
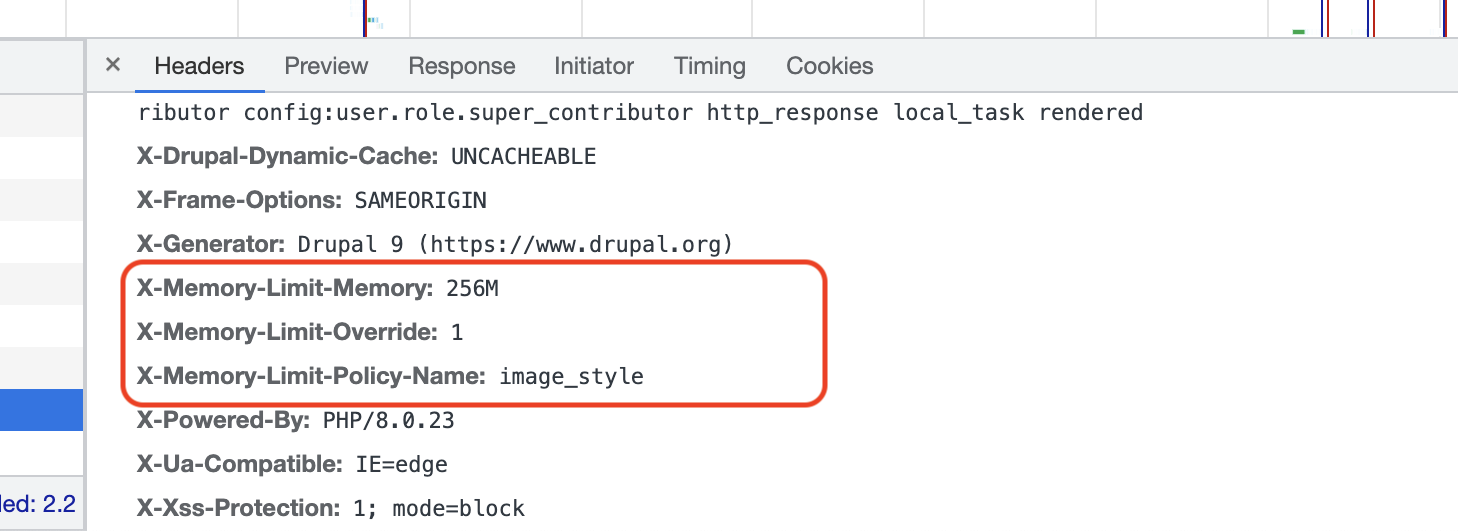
If a policy applies, headers will indicate the name of the policy and the new memory limit applied.
Finally, export the configuration and push to your version control.
id: image_style
label: 'Image style'
weight: null
status: true
memory: 256M
langcode: en
policy_constraints:
-
id: path
negate: false
paths: '/sites/default/files/styles/*'
dependencies: { }